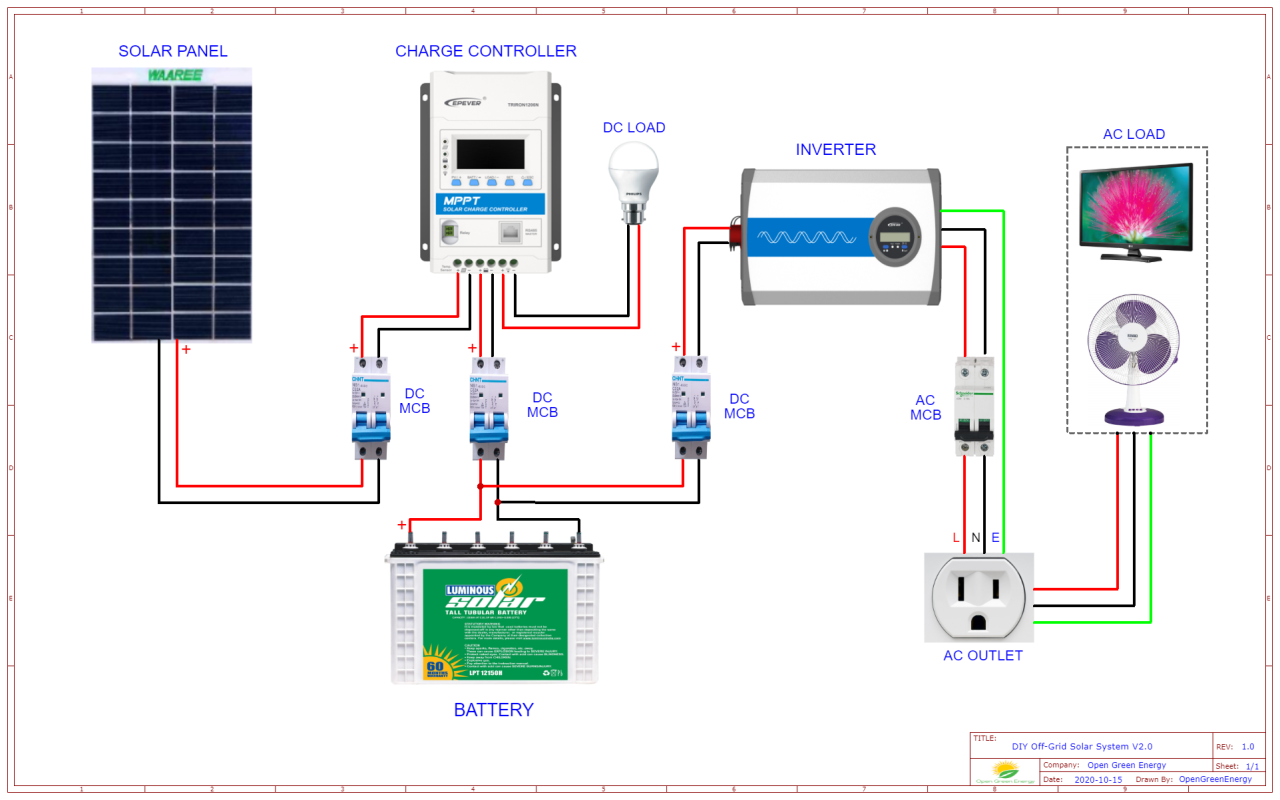
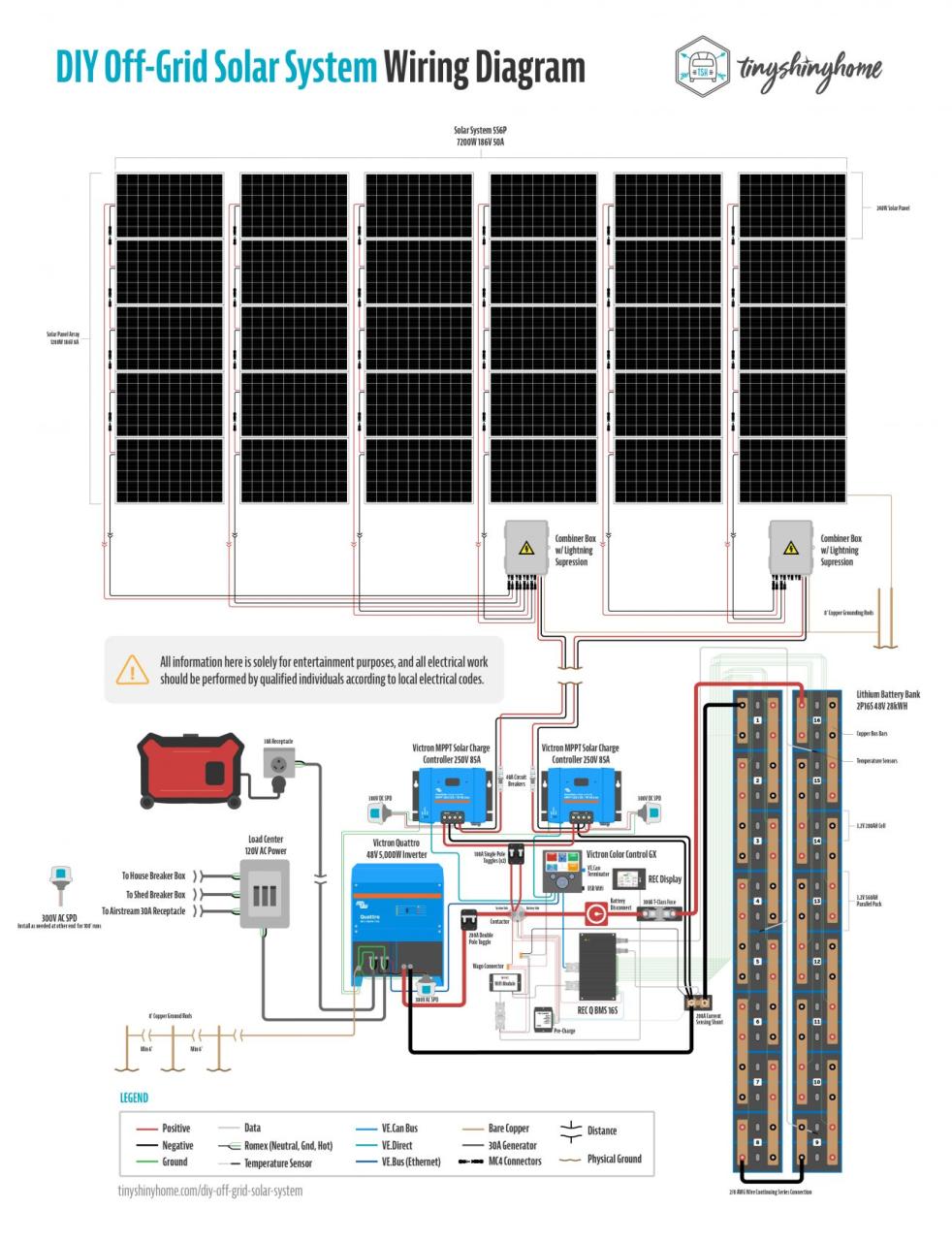
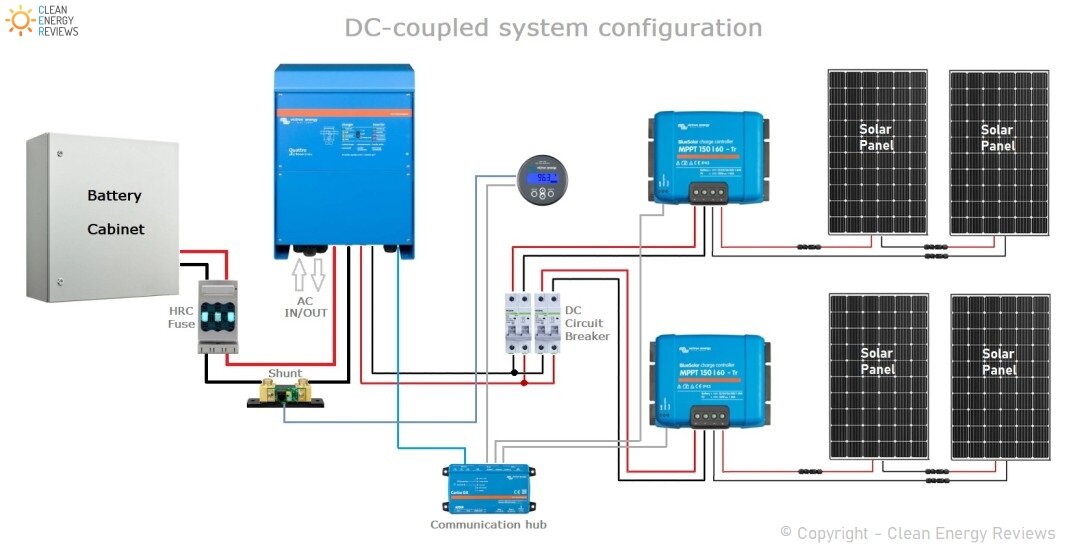
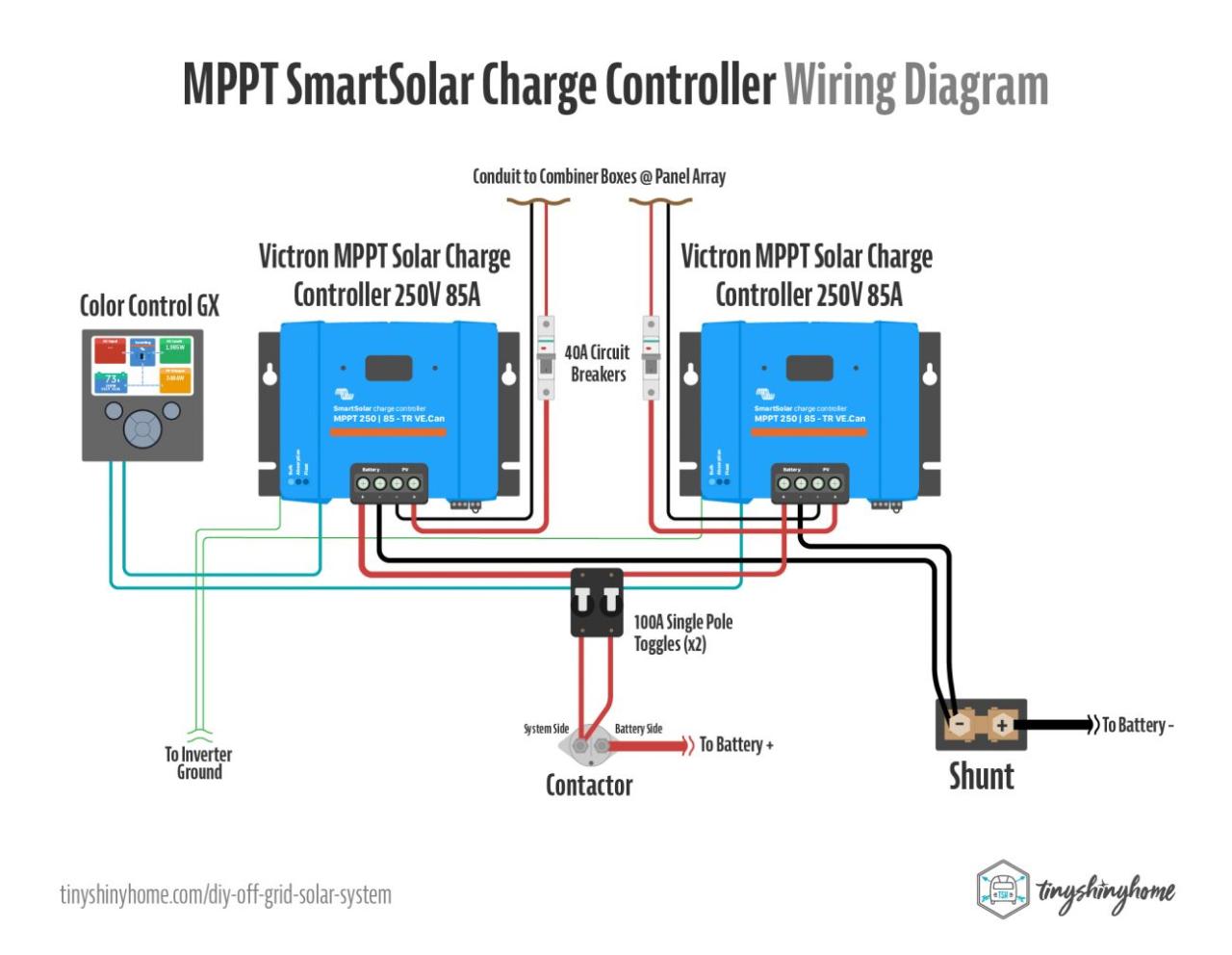
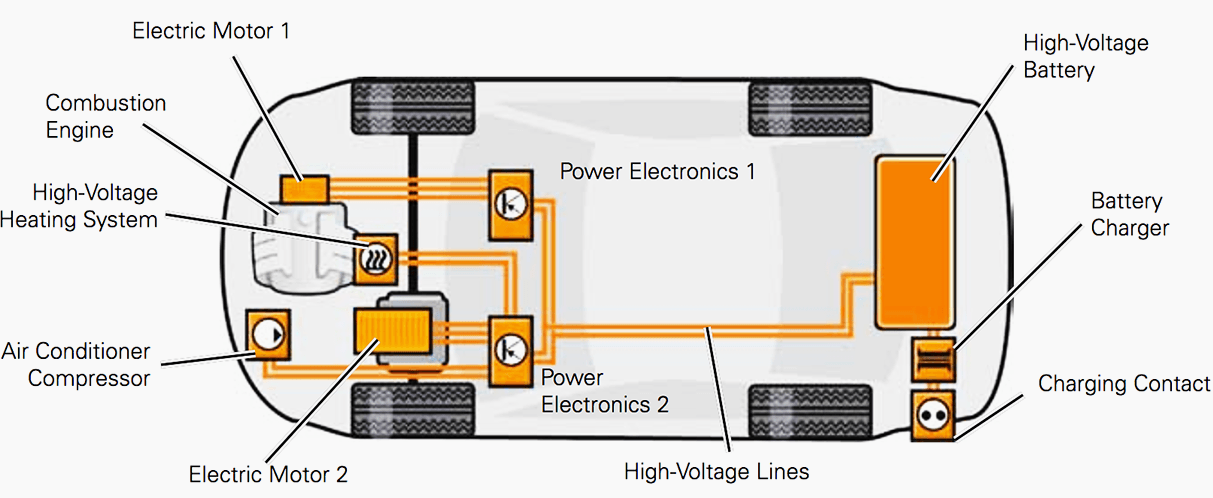
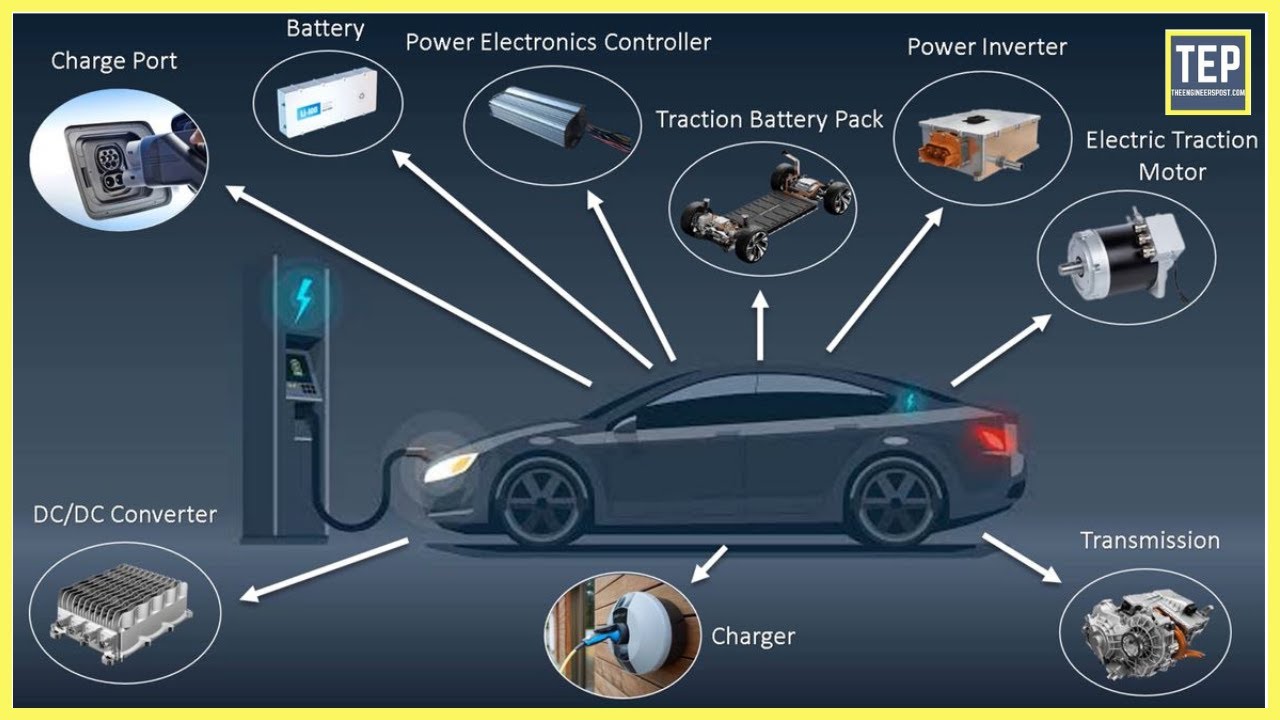
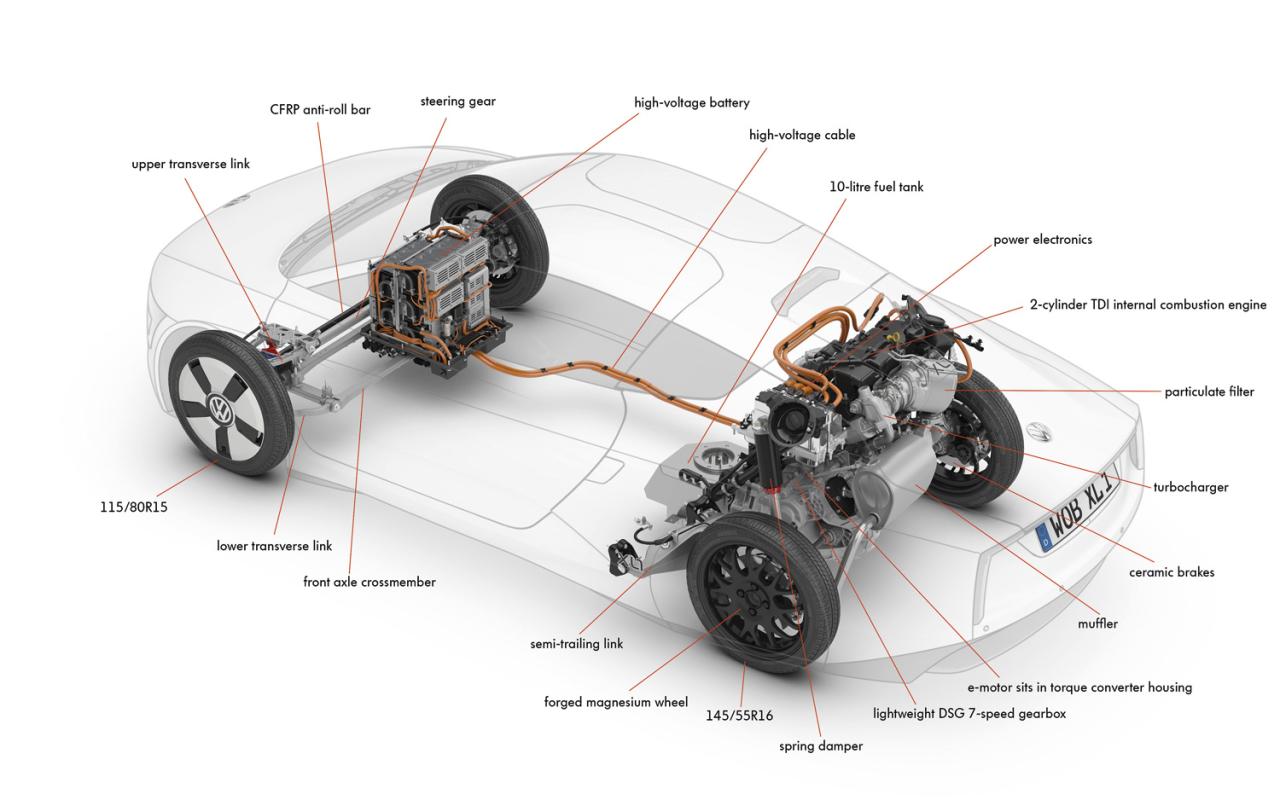
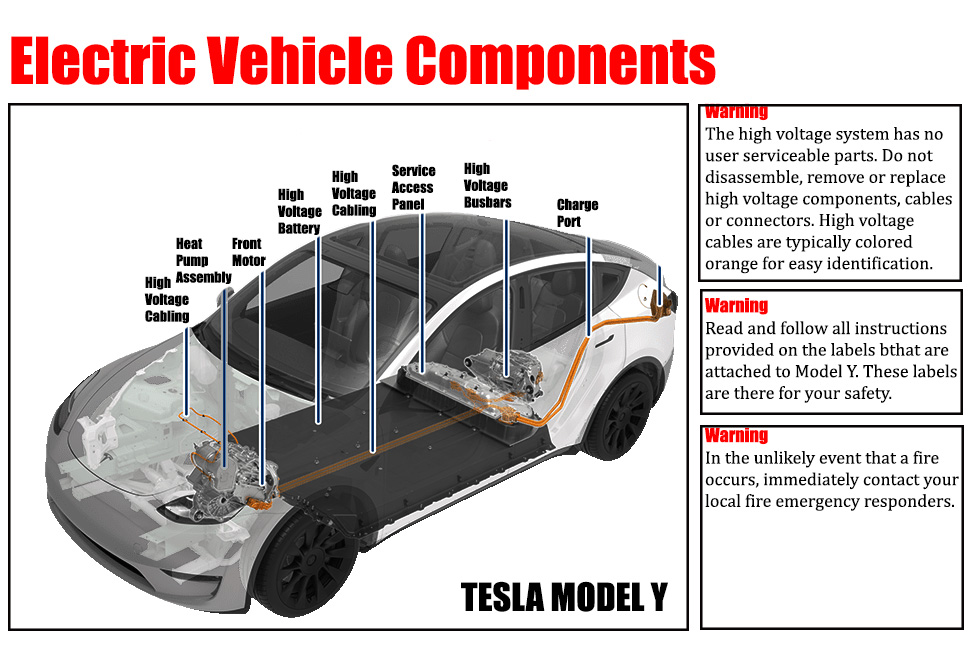
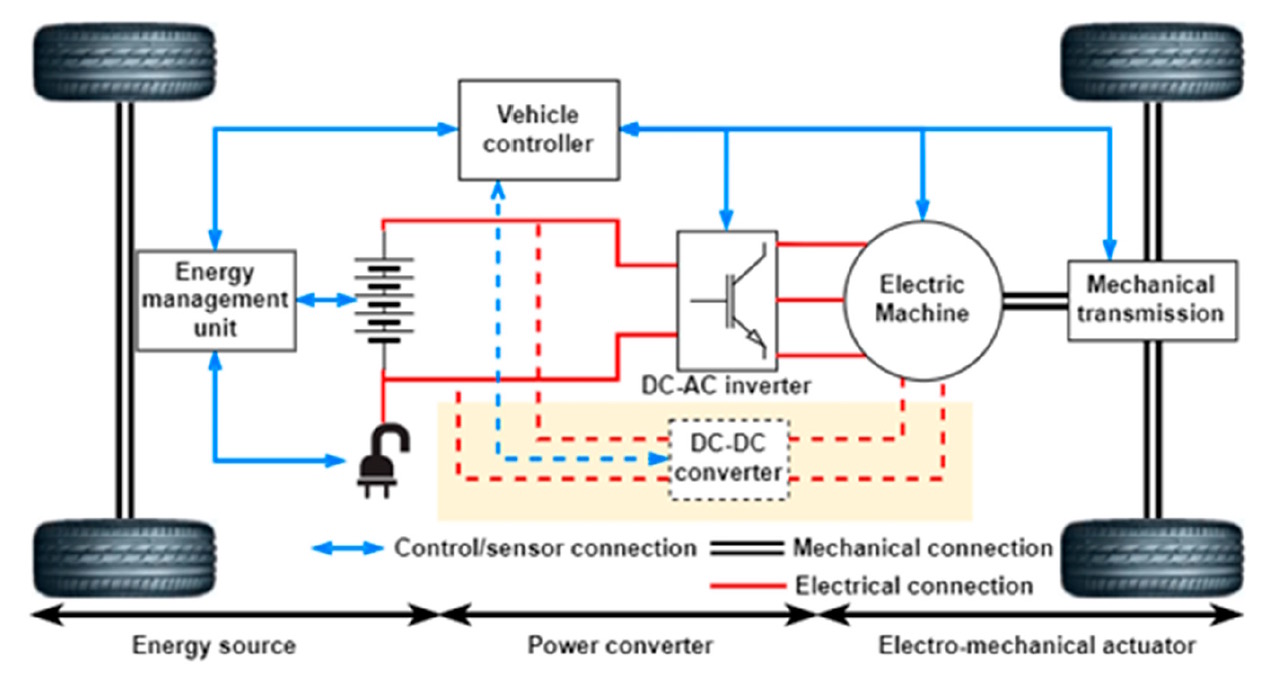
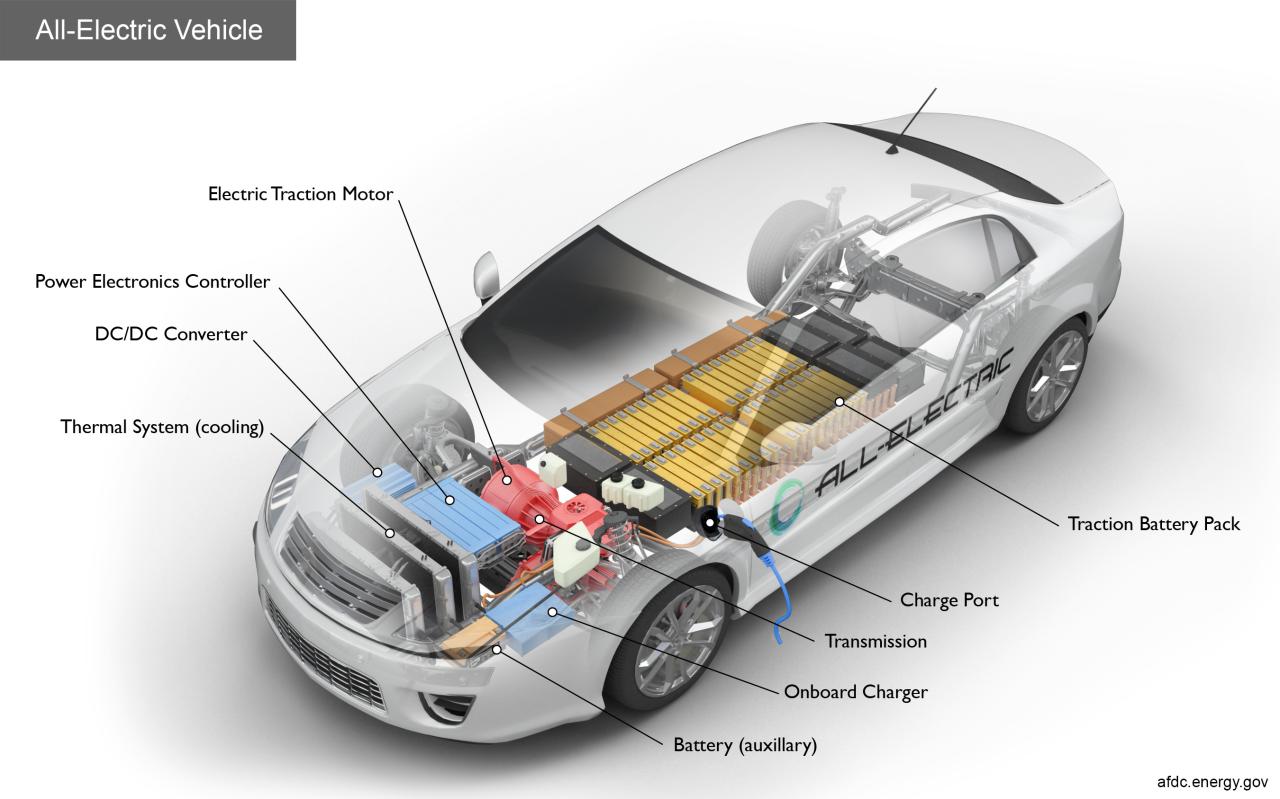
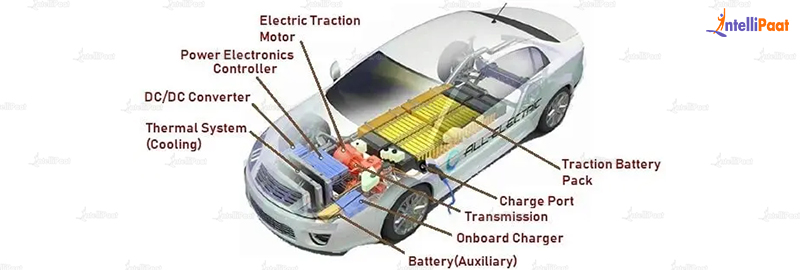
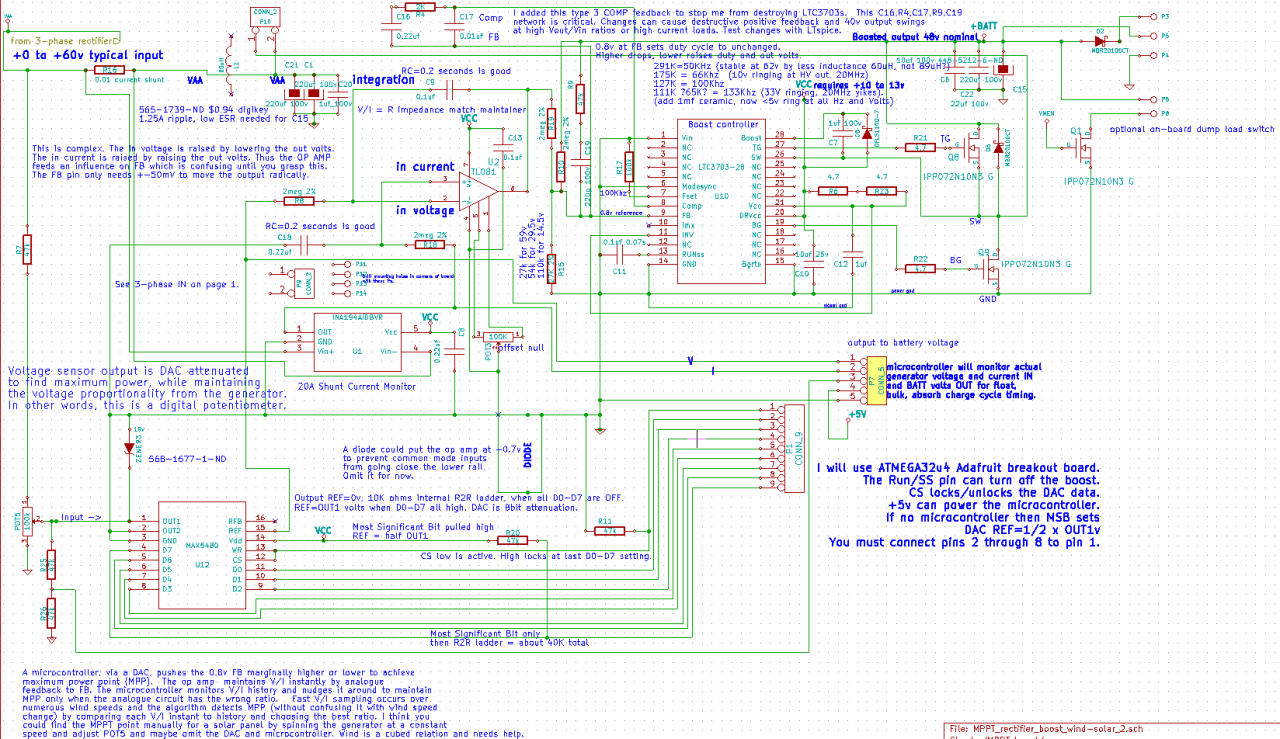
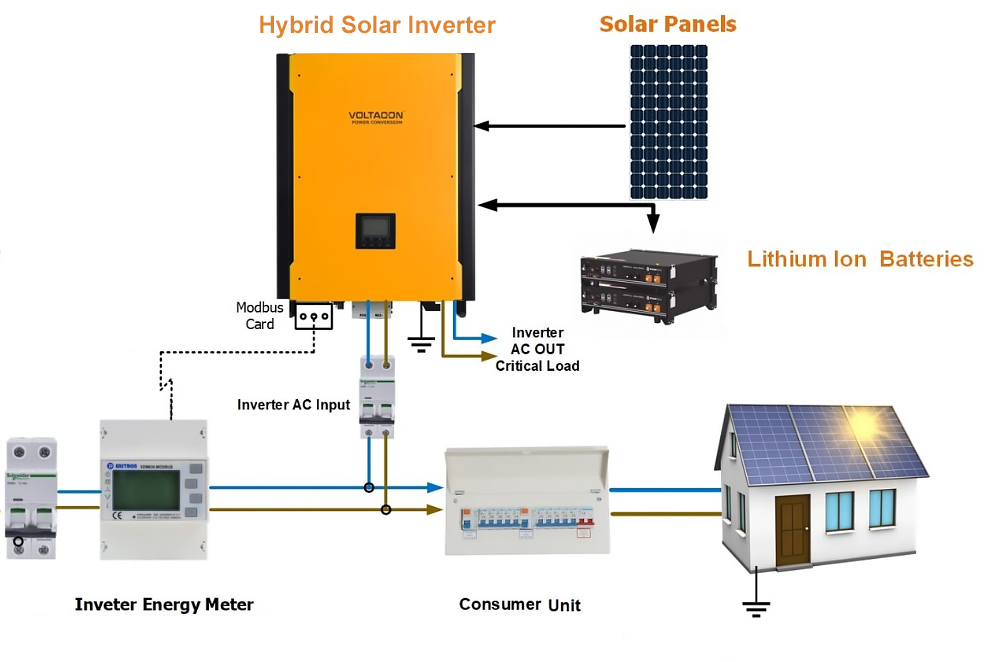
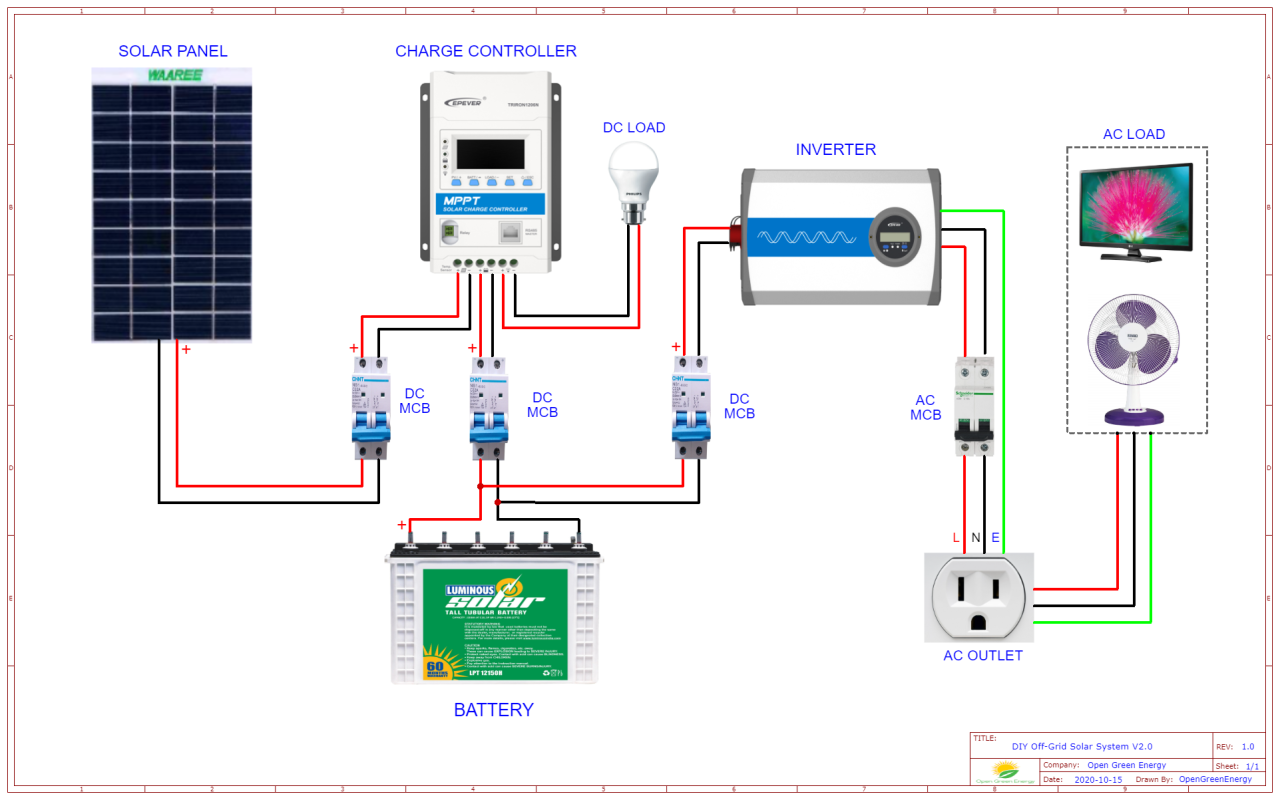
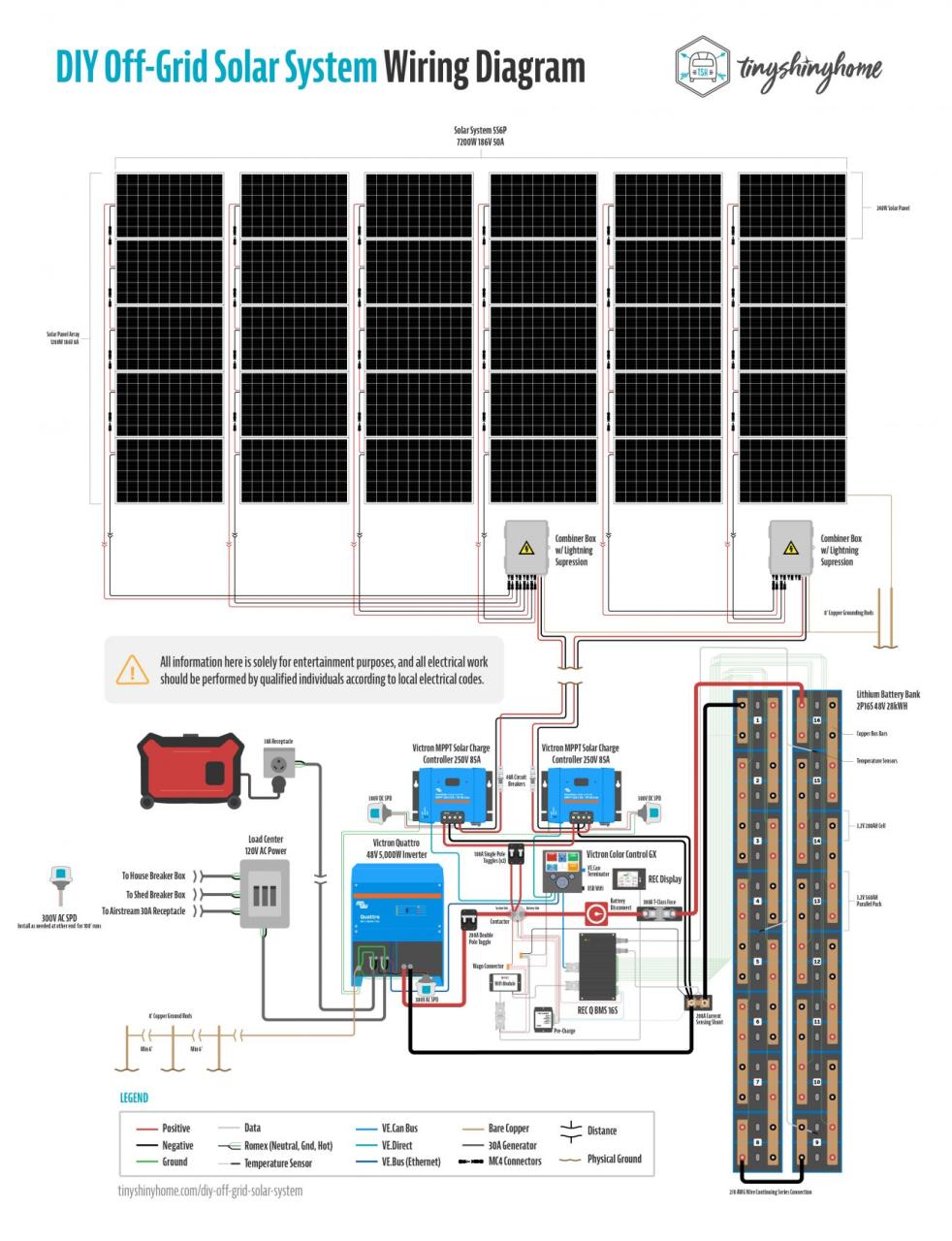
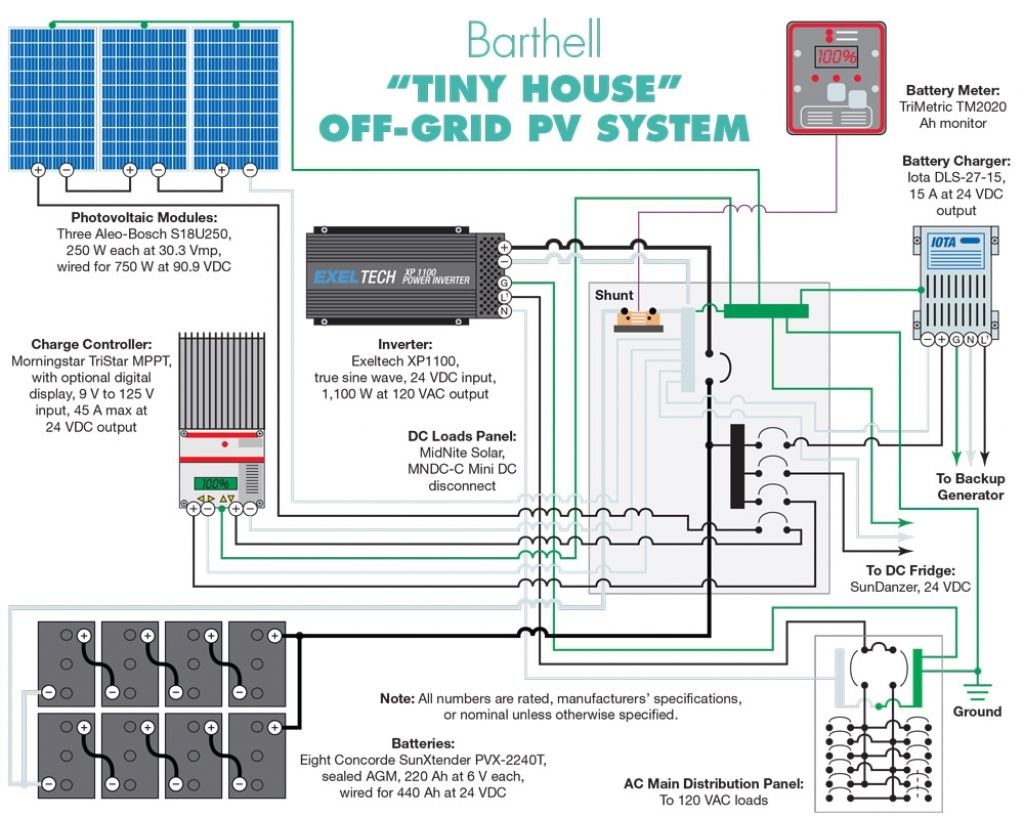
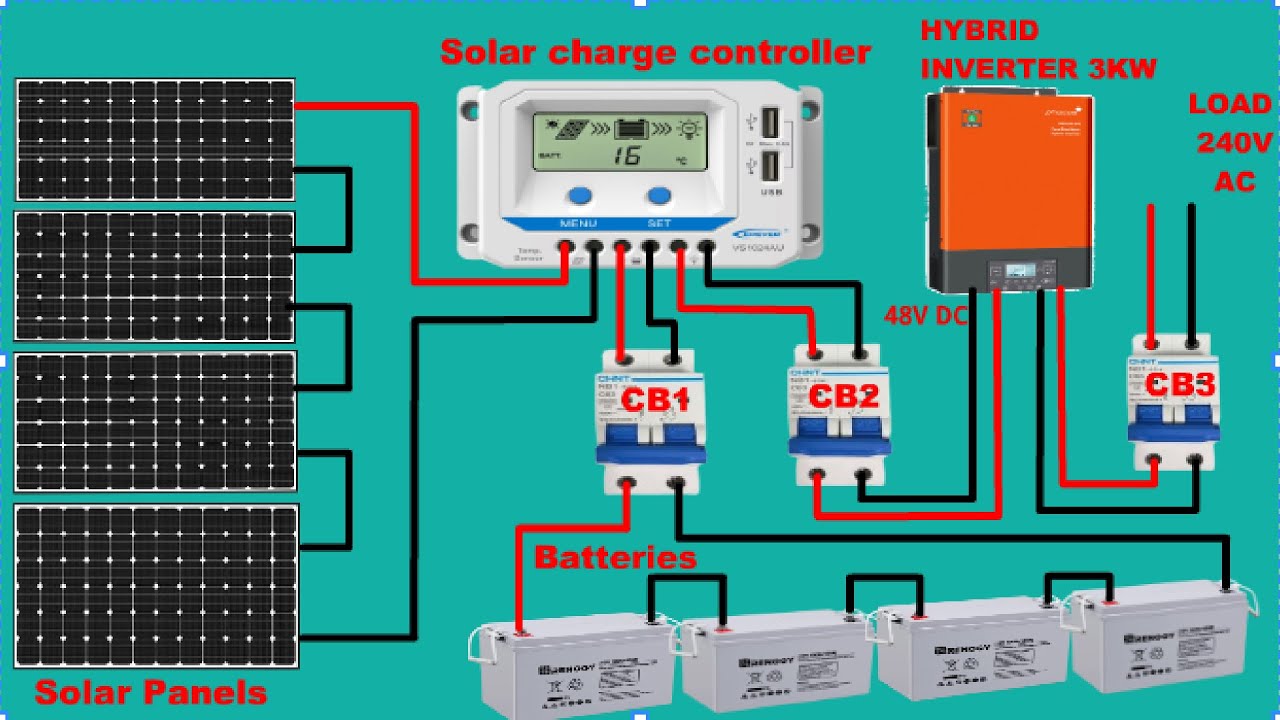
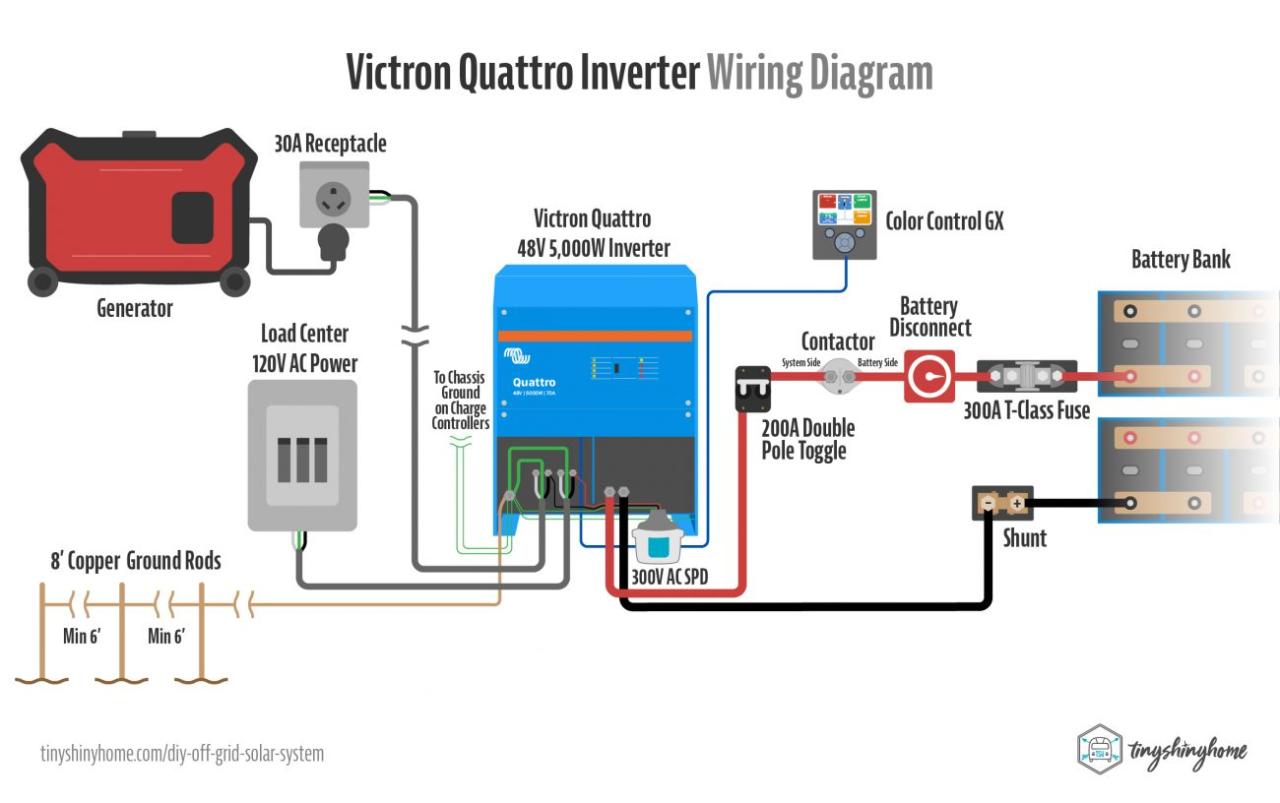
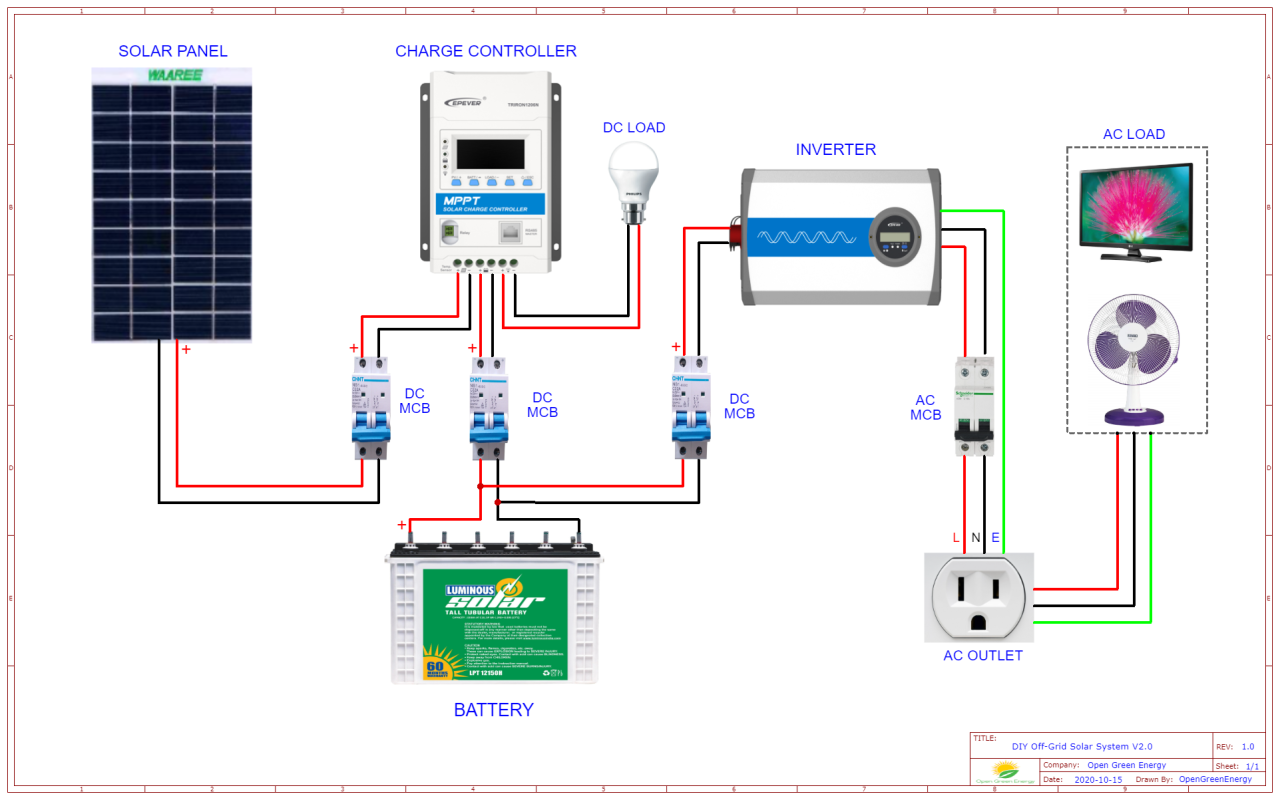
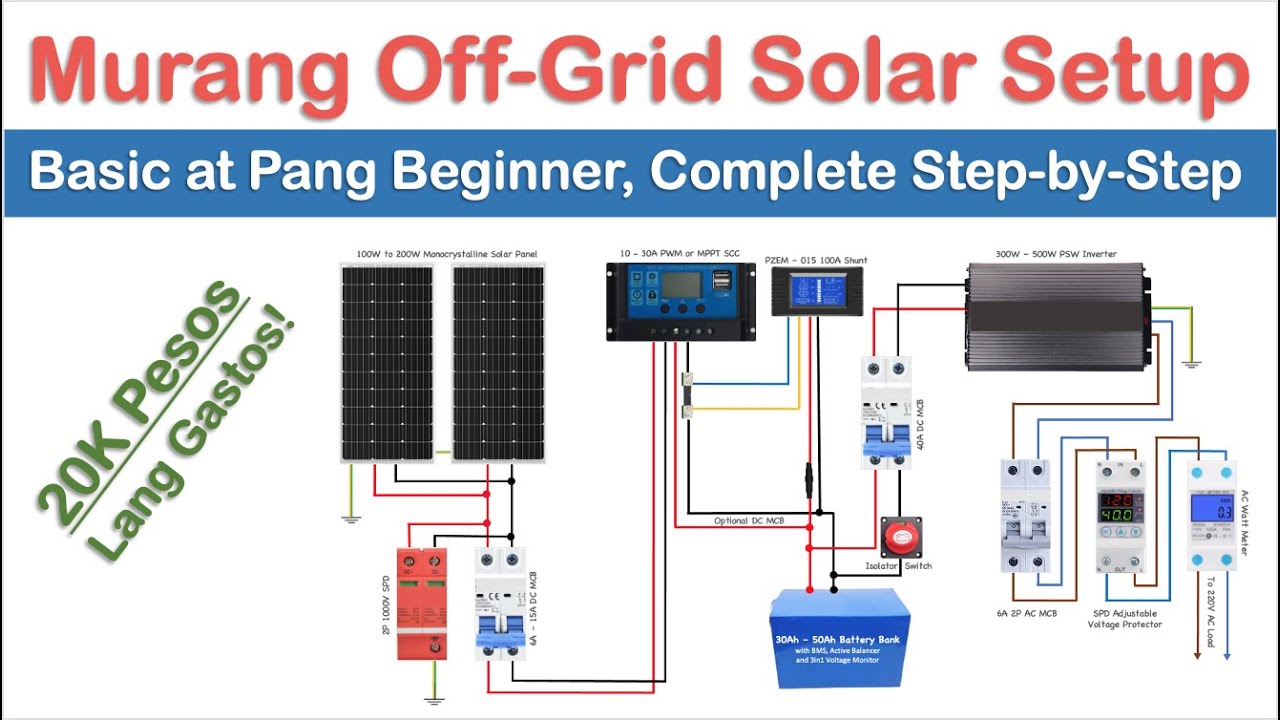
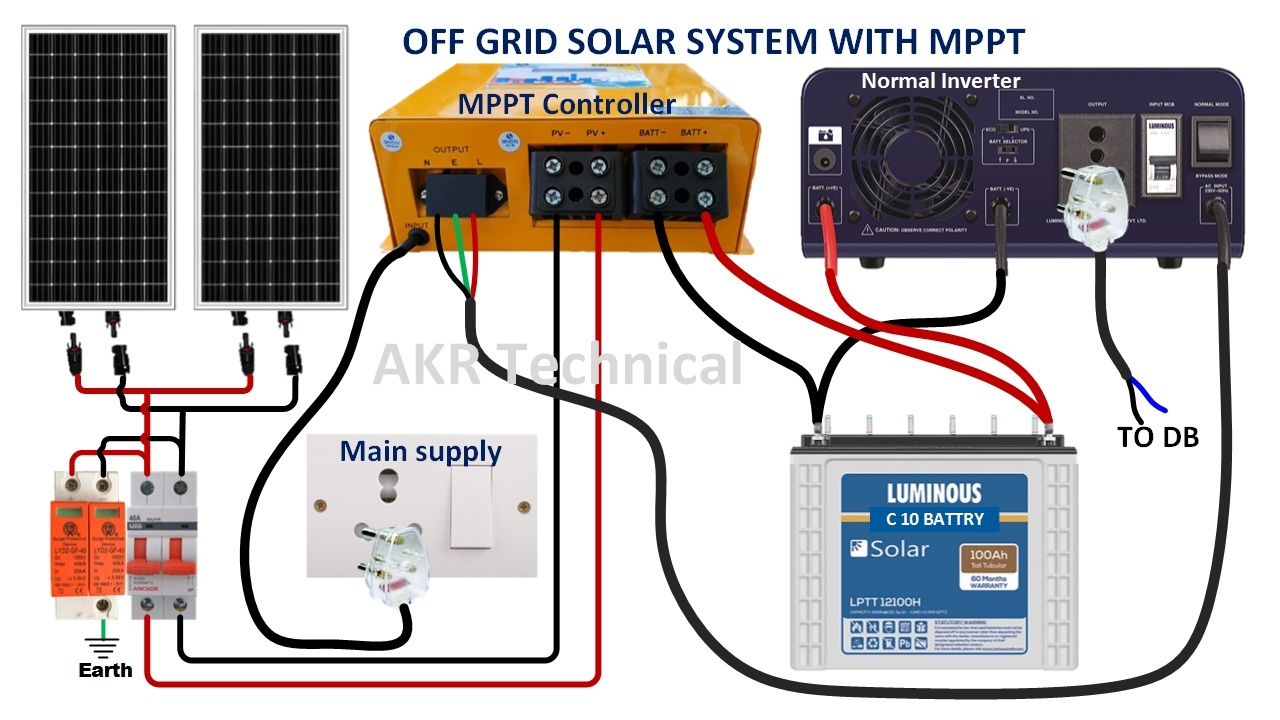
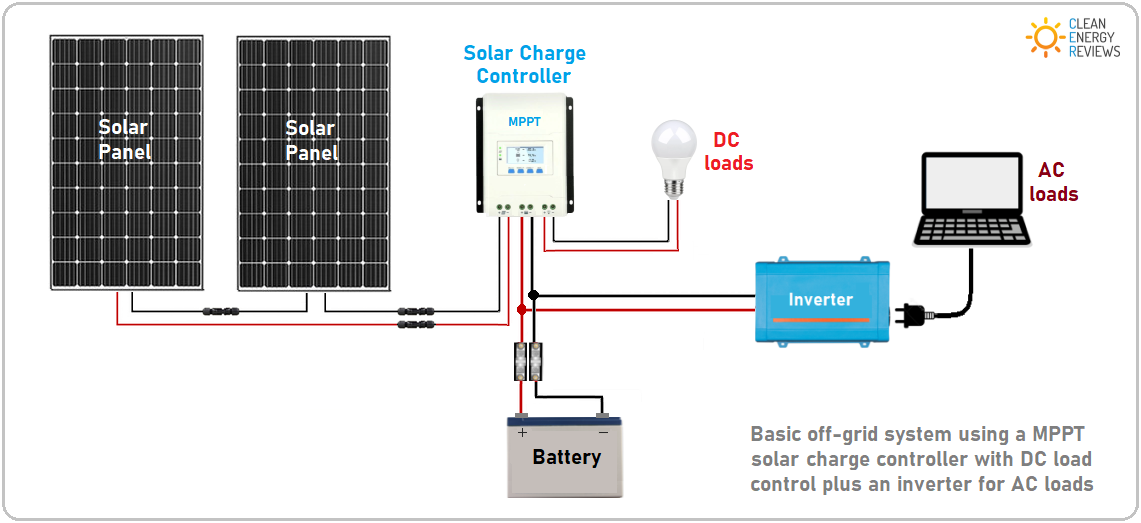
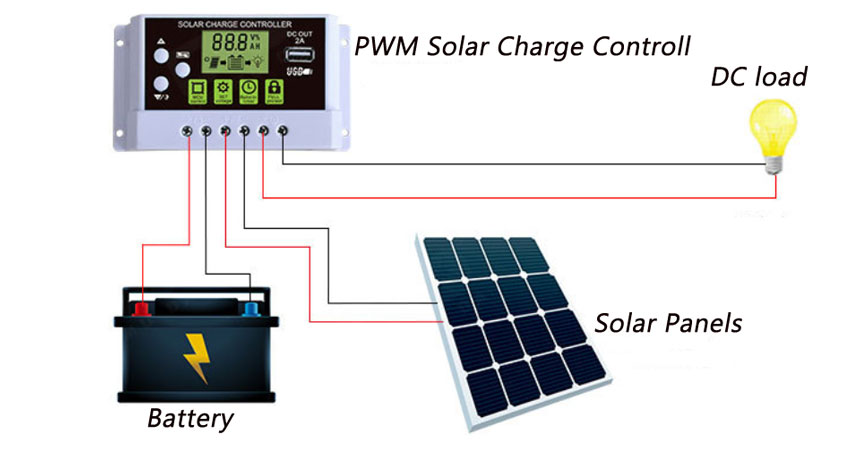
“Connecting solar panels to MPPT controller in parallel
One of the key components of a solar power system is the Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) controller, which plays a crucial role in optimizing energy output. In this article, we will explore the process of connecting solar panels to an MPPT controller in parallel, and provide a comprehensive guide on the benefits, requirements, and best practices for this setup.
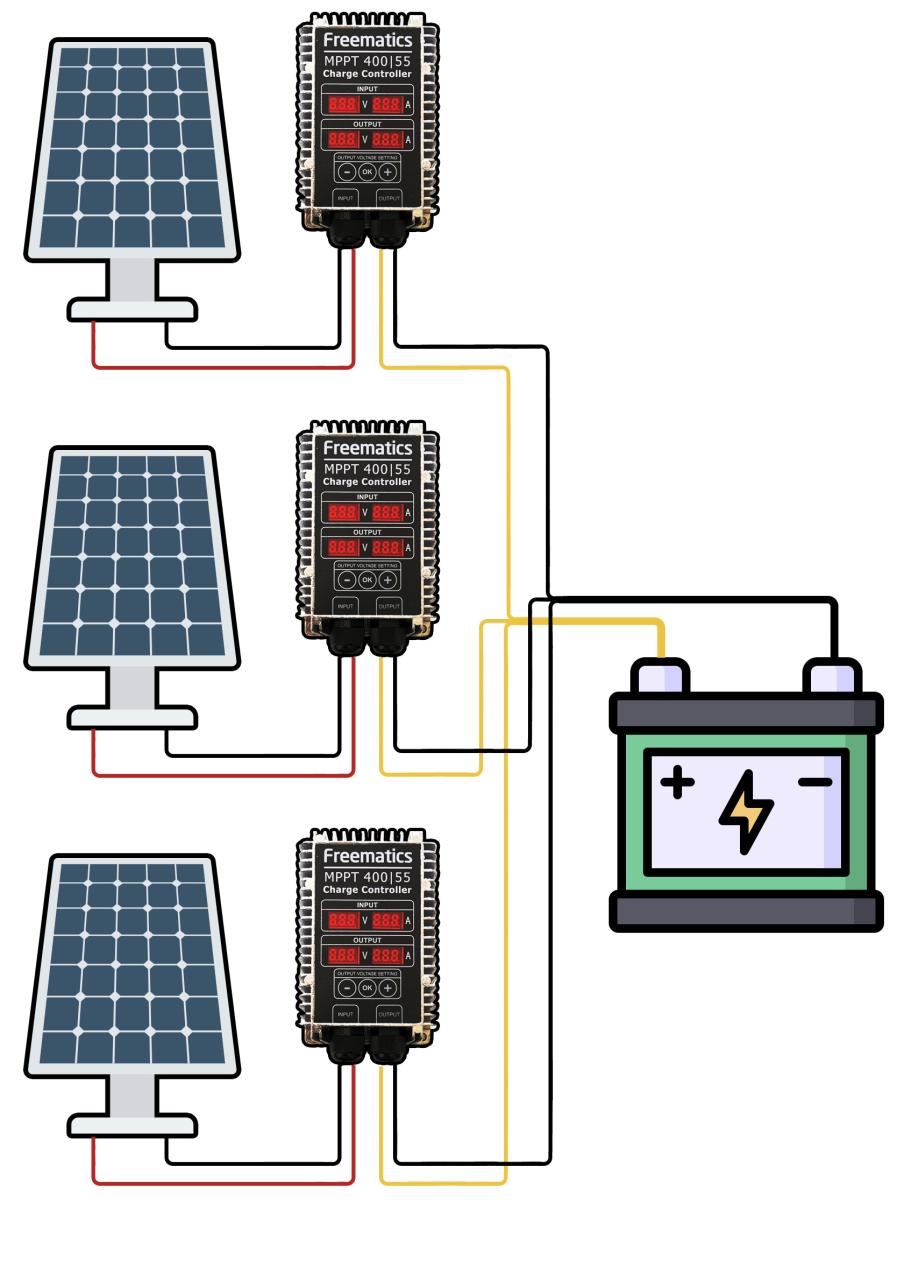
Introduction to MPPT Controllers
Before we dive into the process of connecting solar panels to an MPPT controller in parallel, it’s essential to understand the basics of MPPT controllers. An MPPT controller is a device that tracks the maximum power point of a solar panel array and converts the DC voltage output to a suitable voltage for charging batteries or powering electrical loads. MPPT controllers are designed to optimize energy output by matching the solar panel’s voltage to the battery bank’s voltage, resulting in maximum power transfer.
Benefits of Connecting Solar Panels in Parallel
Connecting solar panels in parallel offers several benefits, including:
- Increased Power Output: By connecting solar panels in parallel, you can increase the total power output of your solar panel array. This is because each solar panel operates independently, and the total power output is the sum of the individual panel’s output.
- Improved System Reliability: When solar panels are connected in parallel, the system can continue to operate even if one or more panels are shaded or faulty. This is because the other panels can still produce power, reducing the impact of individual panel failures.
- Flexibility in System Design: Connecting solar panels in parallel allows for greater flexibility in system design. You can add or remove solar panels as needed, making it easier to upgrade or modify your system over time.
Requirements for Connecting Solar Panels in Parallel

To connect solar panels to an MPPT controller in parallel, you’ll need to ensure that your system meets the following requirements:
- Compatible Solar Panels: Ensure that all solar panels are compatible with each other and have the same voltage rating. Mixing solar panels with different voltage ratings can lead to inefficient energy production and reduced system performance.
- MPPT Controller Compatibility: Choose an MPPT controller that is compatible with your solar panel array’s voltage and current ratings. The MPPT controller should also be able to handle the total power output of your solar panel array.
- Proper Wiring and Connections: Ensure that all wiring and connections are properly sized and secured to handle the maximum current output of your solar panel array.
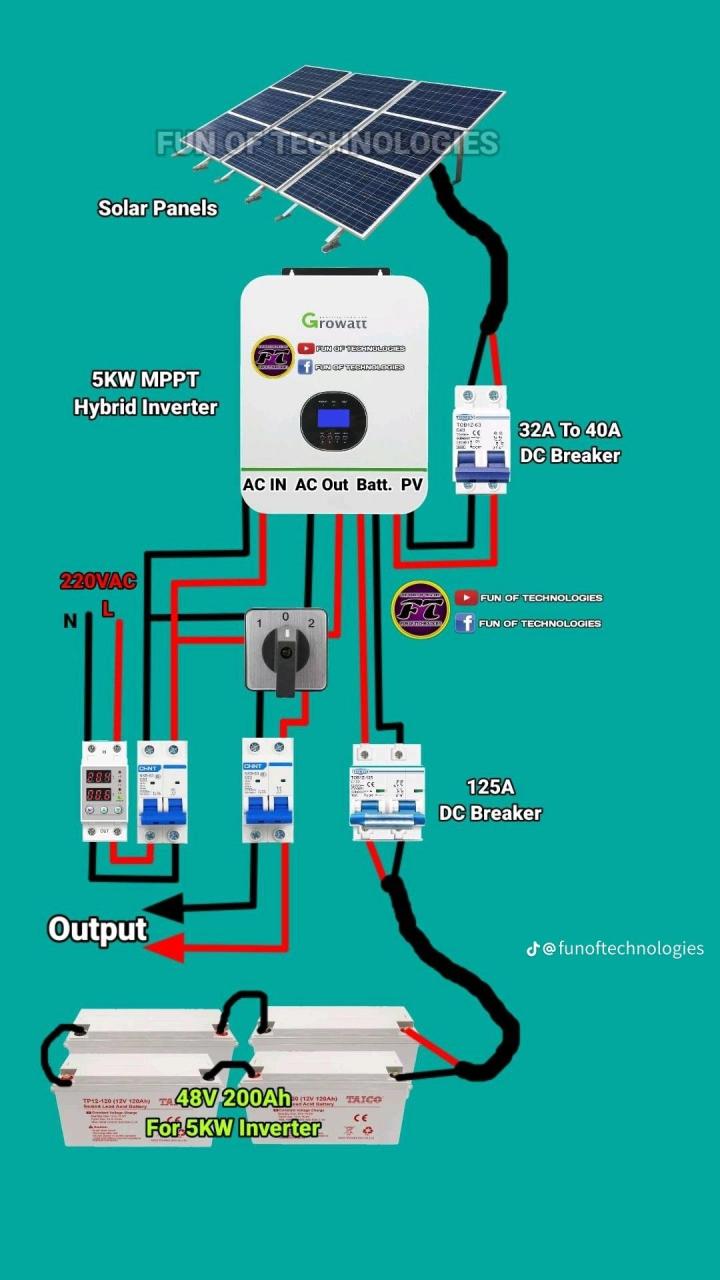
Step-by-Step Guide to Connecting Solar Panels to MPPT Controller in Parallel
To connect solar panels to an MPPT controller in parallel, follow these steps:
- Determine the Total Power Output: Calculate the total power output of your solar panel array by multiplying the individual panel’s power output.
- Choose the Correct MPPT Controller: Select an MPPT controller that can handle the total power output of your solar panel array.
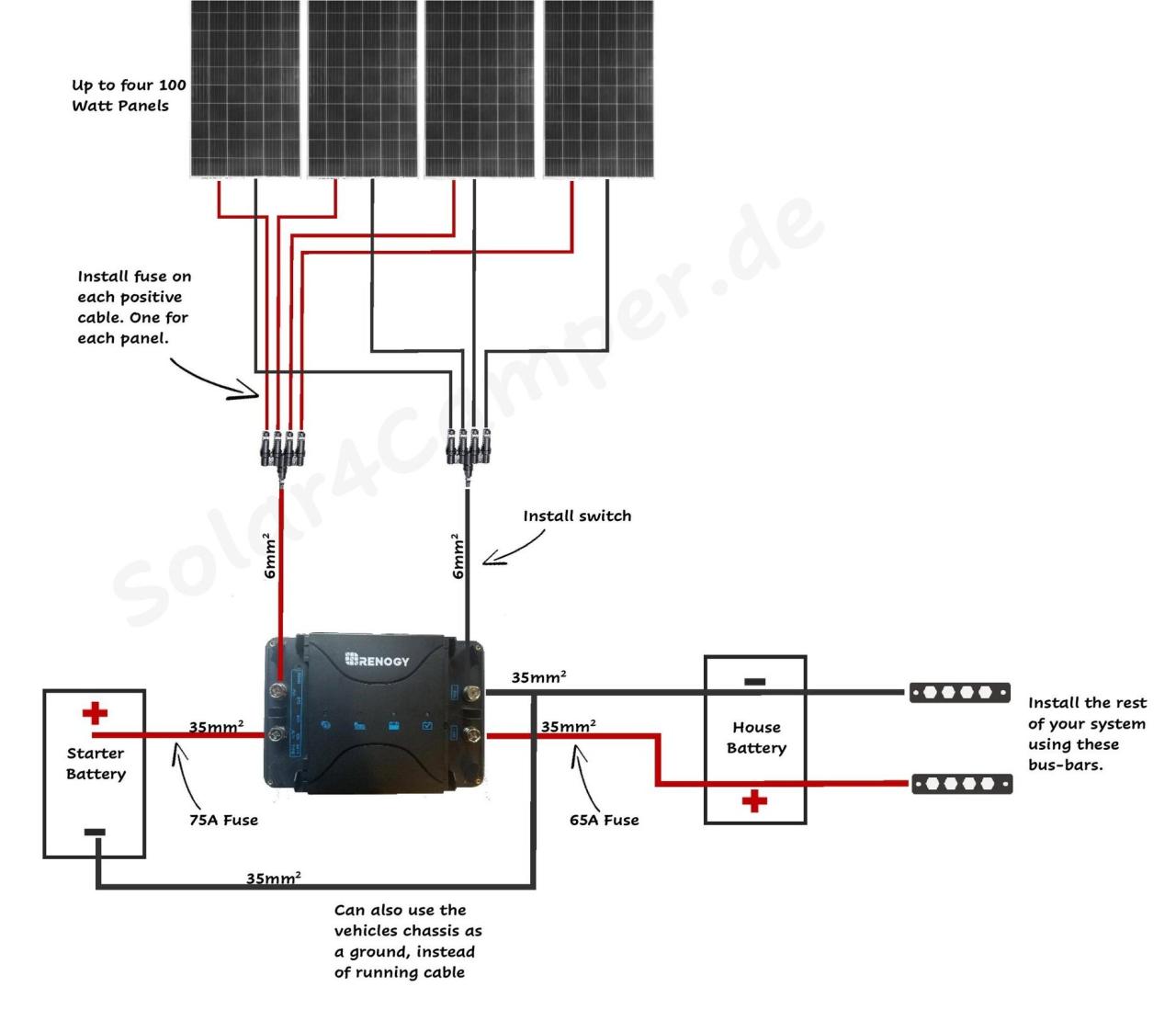
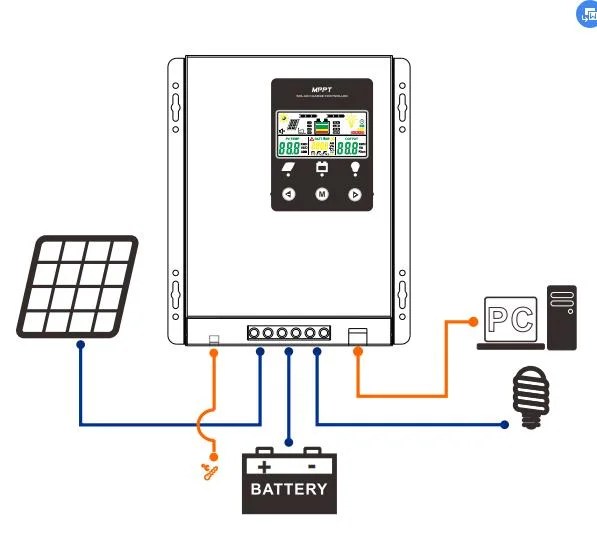
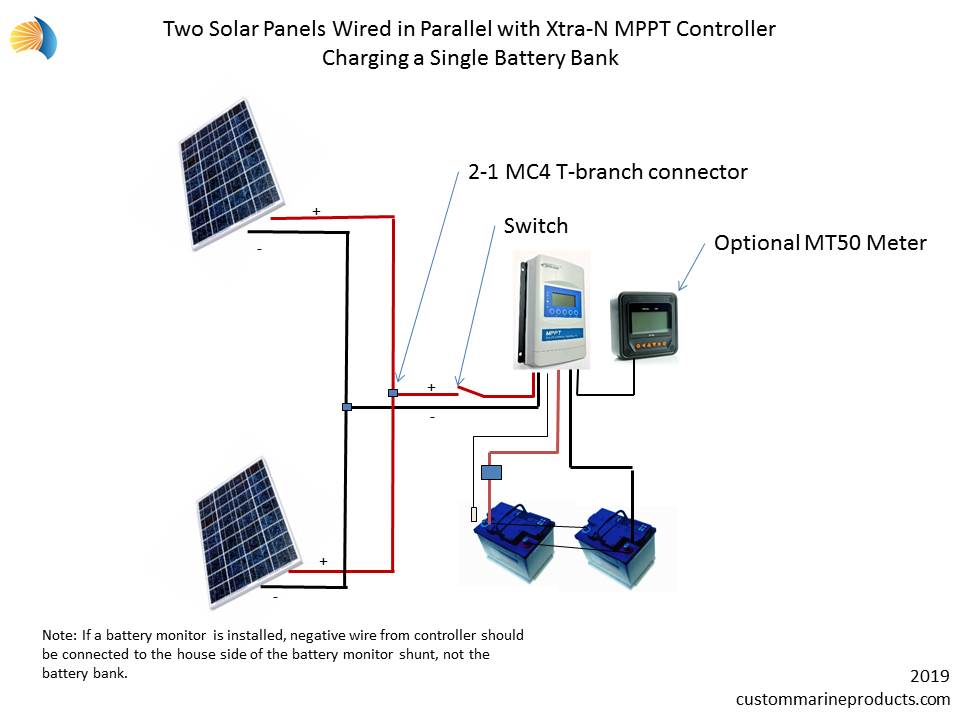
- Connect the Solar Panels in Parallel: Connect the positive terminal of each solar panel to a common positive busbar, and the negative terminal of each solar panel to a common negative busbar.
- Connect the Busbars to the MPPT Controller: Connect the positive busbar to the MPPT controller’s positive input terminal, and the negative busbar to the MPPT controller’s negative input terminal.
- Set the MPPT Controller Parameters: Configure the MPPT controller’s parameters, such as the battery voltage, charging current, and maximum power point tracking (MPPT) settings.
- Test the System: Test the system to ensure that it’s functioning correctly and producing the expected power output.
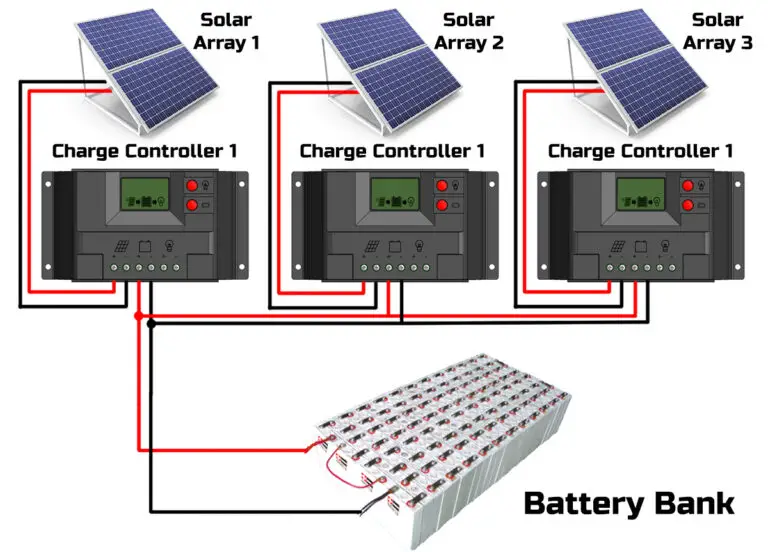
Best Practices for Connecting Solar Panels in Parallel
To ensure optimal performance and reliability, follow these best practices when connecting solar panels in parallel:
- Use Identical Solar Panels: Use identical solar panels to minimize variations in voltage and current output.
- Ensure Proper Wiring and Connections: Ensure that all wiring and connections are properly sized and secured to handle the maximum current output of your solar panel array.
- Monitor System Performance: Monitor system performance regularly to detect any issues or faults.
- Perform Regular Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance tasks, such as cleaning the solar panels and checking the connections, to ensure optimal system performance.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
When connecting solar panels to an MPPT controller in parallel, you may encounter some common challenges and issues. Here are some troubleshooting tips to help you resolve these issues:
- Low Power Output: Check the solar panel’s voltage and current output to ensure that they are within the expected range. Also, check the MPPT controller’s settings to ensure that they are configured correctly.
- High Voltage: Check the solar panel’s voltage output to ensure that it’s within the expected range. Also, check the MPPT controller’s settings to ensure that they are configured correctly.
- Connection Issues: Check the wiring and connections to ensure that they are properly sized and secured.
Conclusion
Connecting solar panels to an MPPT controller in parallel is a great way to increase power output, improve system reliability, and flexibility in system design. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can ensure a safe and efficient connection. Remember to choose compatible solar panels, select the correct MPPT controller, and follow best practices for connecting solar panels in parallel. With proper installation and maintenance, your solar power system can provide reliable and efficient energy for years to come.
Additional Resources
For more information on connecting solar panels to an MPPT controller in parallel, you can consult the following resources:
- Manufacturer’s Instructions: Consult the manufacturer’s instructions for the solar panels and MPPT controller to ensure that you’re following the recommended installation and configuration procedures.
- Online Forums and Communities: Join online forums and communities to connect with other solar power enthusiasts and professionals, and learn from their experiences.
- Technical Guides and Manuals: Consult technical guides and manuals to learn more about solar power systems, MPPT controllers, and parallel connections.
By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this article, you can create a reliable and efficient solar power system that meets your energy needs and provides a sustainable source of power for years to come.